MOJ
eISSN: 2374-6939


Research Article Volume 16 Issue 5
1Senior Consultant (Physiotherapy) at Star Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation Centre, Bangladesh
2Senior Consultant (Physiotherapy), New Life Trauma Centre, Bangladesh
Correspondence: Mohammad Amanullah Azad, Senior Consultant (Physiotherapy) at Star Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation Centre, Mirpur, Dhaka, Bangladesh , Tel +8801715527946
Received: October 08, 2024 | Published: December 11, 2024
Citation: Azad MA, Rashid MH. Knowledge, attitude and practice around the threat influences of Cardiovascular Disease among the younger adults of Mymensingh District in Bangladesh. MOJ Orthop Rheumatol. 2024;16(5):264-269. DOI: 10.15406/mojor.2024.16.00683
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) interpretation for 27.93% of entirely demises trendy Bangladesh. Foremost risk factors for CVD contain age, gender, heredity, hypertension, cigarette smoking, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, obesity and physical dormancy. The recent study was steered to appreciate the knowledge, attitude and practice (KAP) of younger adults regarding cardiovascular diseases. This is a cross-sectional study exhausting a convenience sampling technique. The sample size was 55. KAP questionnaire remained advanced formerly scattered to the respondents involved. The data composed stood scrutinized using SPSS version 22.0. The mean and standard deviation of the knowledge, attitude and practice grooves were 37.89±5.811. Substantial difference on knowledge marks stood create amongst diverse risk factors (p<0.001), also on attitude and practice nicks in comparison amongst altered genders (p = 0.005 and 0.017, correspondingly). This study also shows a momentous constructive association between attitude and practice nicks (r=+0.354, p<0.001). Are you conscious of record useful method for retrieval this study showed that physiotherapy participants were chief rate that was 41.8% (n=23) and both participants were 40% (n=22) and medication were 18.2% (n=10). In this research should recommend and inspire in exercise further and ripen a healthier lifestyle.
Keywords: CVD, KAP, Risk factors, warning symptoms
CVD, cardiovascular disease; KAP, knowledge, attitude, practice; KSA, kingdom of saudi arabia; SES, socioeconomic status; SPSS, statistical package for the social sciences; USD, united states dollar; WHO, world health organization
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) continue to be the leading cause of death worldwide.1 CVD stands answerable in lieu of 30% of wholly expiries trendy Malaysia with hypertension glaze the slant.2 CVD remains the foremost basis of expiries in sundry evolving realms equally glowing. Threat issues for cardiovascular disease remain alienated obsessed by dual classes; foremost and trifling causative influences.3 High blood pressure, smoking, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, and physical indolence are the main risk factors. Strain, sex hormone imbalance, use of genetic control pills, and alcohol intake are among the factors that may have an impact on trivial underwriting.4 Age, sex and inheritance remain likewise acknowledged as non-amendable menace elements. Extra reasons such as smoking, fatness and bodily dormancy canister stay reflected as per adjustable threat features since it canister be measured and reformed.5 It is the number one cause of morbidity and mortality world-wide. The pecuniary bearing of diverse types of CVD is giant. Traditionally, Bangladesh is a developing country hampered with transmissible diseases. Still, like many other low-income countries in the world, she has been suffering epidemiological conversion; the dominant disease configuration is fluctuating from contagious diseases to non- communicable diseases (NCD).6,7 In addition to its danger effects, the total number of young people with severe CVD has become a major concern as expansion has progressed in a number of developing countries, including Malaysia. To date, raising awareness of cardiovascular disease among younger people is crucial to reducing its prevalence. Therefore, it is still likely that young people will observe strong regimes.8 Weighing standard Knowledge attitude and practice of young person’s such as institutional scholars with resident peoples on CVD matters are vital then crucial. Several revisions of KAP stood conducted to comprehend the outline of the ailment existence and its comportment amid civilization. A conflicting impost on KAP, its features besides considerate is long-suffering in foiling and imposes an enduring espousal of a strong lifestyle.9 This learning is determined by dividing the KAP among young adults in Bangladesh's Mymensingh District according to the threats of cardiovascular disease (CVD), linking the KAP stages to changed sociodemographic characteristics, and then assessing the relationship between the Knowledge Attitude Practice and the Threat Aspects of Cardiovascular Disorder.
Resources and procedures
Study plan
This investigation prioritized a cross-sectional analysis of demeanor usage over a quantitative enlightenment approach. Cross-sectional trifling purpose was chosen as a legitimate method of data collection in order to meet the study goal.
Study area
Mymensingh District's sequestered hospital, Mymensingh Medical College Hospital, and various physiotherapy Centre’s.
Study Population:
Participants in this study were trendy Bangladeshis aged 20 to 32 who lived in the Mymensingh district.
Sample extent
P= pervasiveness of Bangladeshi knowledge, attitude and practice trendy threat influences transitory cardiovascular ailment (aggregate (ratio) of the over-all people)
p= 20.5% (Populace census-2001)
q= 1-p
q=1-.20.5
=0.80
d= adequate brim of blunder (.05)
The dimensions of the authentic image were maintained.
(n) = Z² pq/d²
= (1.96)² × 0.5 × 0.5/ (0.05)²
= 3.84 × 0.25 / 0.0025
=384
As a result, 55 remained set aside as the taster of this task since Mymensingh Medical College Hospital and the private chamber of physiotherapy Center with Cloistered Hospital in Mymensingh district, rather than drilling as a fragment in a speculative exploration venture. The number of clarifications or participants in a study or research is known as the sample size. In my city, young adults engage, but there was a high level of focus on empathetic and treatment hitches. This sample population is robust and voluntarily participated.
Sampling method
Samples remained preferred castoff convenience taster method.
Insert norms
Exclusion criteria
Data assembling tool
The questioner primed the data in a well-structured form, and the scrutiny panel approved it. The baseline material was calm, and the interrogator supervised the entire man-to-man discussion.
Technique of statistics crew
Data was created by the scholar through personal connection and discussion. The discussion was conducted in a confidential manner as much as feasible. In addition, the study's aspects were explained to the qualified accused and familiar engraved agreements obtained from the accused prior to the data collection. The conversation took place in a quiet home, and no one else was allowed to influence the defendant's response. It set aside a standard twenty minutes to cover the entire talk of a single defendant.
Data scrutiny
Data remained analyzed. Version 22.0 of the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS). Tables, bar graphs, pie charts, and other visual aids were embellished using Microsoft Office Excel 2013 and version 15.0. Trendy, quantitative data was still included in the outcomes of the advanced amendment. In an auspicious sense, there was some indication that was peaceful.
Multiplication of Chi-Square
The total of the square variance (O — E) 2 between the observed (O) and expected (E) data that deviates from the expected (E) data by substance succeeding equality is known as chi square (x2) in completely plausible data;
(Observed count – Expected count) 2
Expected count
(O —E) 2
(x2) =
E
The calculated code, the method appearances identical this:
Ethical consideration
This critique's intended methodology was carried out by subsequent World Health Organization (WHO) investigation strategies and Bangladesh Medical Research Council (BMRC) procedures. Approval because the study was scheduled to be deported by the principal of Mymensingh Medical College Hospital.
Acquainted consent
Prior to the questionnaire's end, a postscript requesting transcribed consent was presumed for each contestant. Each accomplice signed to reserve the carved deal. The accomplices were obviously aware that their testimony would be kept secret and reticent.
|
Class |
Frequency |
(Percentage)% |
|
SSC |
5 |
9.1 |
|
HSC |
23 |
41.8 |
|
Graduate |
23 |
41.8 |
|
Masters |
4 |
7.3 |
|
Total |
55 |
100.0 |
Table 1 Distribution of respondents education (n=55).
This table showed that the chief level of HSC and graduate members remained at 41.8% (n=23). The highest frequency for SSC participants maintained 9.1% (n=5), while the highest frequency for Masters Contestants remained 7.3% (n=4). We have discovered that the participants' educational qualifications in this segment are rather reasonable.
According to the study, the average age of the interviewee was 37.89 years (SD± 5.811). The age of the trendiest accused is almost 30 years old, followed by 50 years old. There is about 33.76 years of inconsistency.
Of the 55 respondents, the largest percentage (53%) of accused people were between the ages of 20 and 25. The lowest percentage (18%) of accused people were between the ages of 31 and 35. In terms of age range, the extremely young and highest numbers are the highest. The two groups most pertinent to the study's essential focus are young people).
Figure 3
At the time of the vogueish depiction, the number of male and female accomplices was equal. There were 74.5% females (n=41) and 25.5% males (n=14). Women are far ahead in terms of research expertise because of the number of them and their active participation.
|
|
Frequency |
(Percentage)% |
|
Unemployed |
33 |
60.0 |
|
Service |
20 |
36.4 |
|
Business |
2 |
3.6 |
|
Total |
55 |
100.0 |
Table 2 Distribution of respondents occupations (n=55)
This data revealed that the top frequency of unemployed opponents was still 60.0% (n=33). The leading rate for service contributors stayed at 36.4% (n=20), followed by business opponents at 3.6% (n=2). Instead of refusing to participate completely in this study and make use of their skills, the unemployment rate among the participants was fairly high in this instance.
This statistic showed that no contestants remained 36.4% (n=20) while yes participants retained the highest frequency, standing at 63.6% (n=35). According to this study, stroke sufferers require immediate treatment, and the yes participants strongly supported the notion that stroke could be treated.
|
|
Frequency |
(Percentage)% |
|
Yes |
31 |
56.4 |
|
No |
24 |
43.6 |
|
Total |
55 |
100.0 |
Table 3 Distribution of respondents in cerebral stroke an emergency requiring medical management as is the case for cardiac attack (n=55)
According to this table, the highest frequency of participants who stood up was 56.4% (n=31), followed by those who did not stand up at 43.6% (n=24). In the event of a heart attack, cerebral stroke requires immediate medical attention. Indeed, individuals were chosen from a higher level, and the level of urgency was deemed acceptable.
|
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
Hypertension |
24 |
43.6 |
|
Smoking |
18 |
32.7 |
|
Vascular rupture |
1 |
1.8 |
|
Familial history |
2 |
3.6 |
|
Arrhythmia |
4 |
7.3 |
|
Obesity |
1 |
1.8 |
|
Myocardial infraction |
2 |
3.6 |
|
Thrombosis |
1 |
1.8 |
|
Nervousness |
1 |
1.8 |
|
Hyper triglycerdemia |
1 |
1.8 |
|
Total |
55 |
100.0 |
Table 4 Distribution of respondents Are you aware of risk factors that predispose to stroke (n=55)
According to this table, candidates with hypertension maintained the highest ratio, which remained at 43.6% (n=24), while those who smoked maintained the second-highest ratio, which remained at 32.7% (n=18). The third chief ratio, which maintained at 7.3% (n=4), was arrhythmia. MI and family history were 3.6% (n=2) and 3.6% (n=2), respectively. Obesity, thrombosis, hypertriglyceremia, and vascular rupture all remained 1.8% (n=1). As demonstrated here, smoking and high blood pressure were the two main risk factors for stroke, but obesity was less of a risk factor.
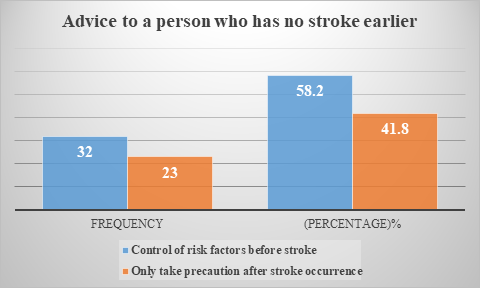
Figure 5 Distribution of respondents what will be your advice to a person who has no stroke earlier (n=55).
This figure presented that participants who controlled risk factors prior to having a stroke maintained their peak speed for 58.2% of the time (n=32), while those who only took precautions after having a stroke remained for 41.8% of the time (n=23).
|
|
Frequency |
(Percentage)% |
|
Wait and see |
23 |
41.8 |
|
Ask for medical next day |
25 |
45.5 |
|
Ask for medical care immediately |
6 |
10.9 |
|
Call a doctor |
1 |
1.8 |
|
Total |
55 |
100.0 |
Table 5 Distribution of respondents what would you do if you to be suspected to be a having stroke (n=55)
This table showed that participants who received physiotherapy maintained the highest level, remaining at 41.8% (n=23), whereas contestants who received medication maintained at an equal rate of 40% (n=22) and 18.2% (n=10).
|
|
Frequency |
(Percentage)% |
|
Medication |
10 |
18.2 |
|
Physiotherapy |
23 |
41.8 |
|
Both |
22 |
40.0 |
|
Total |
55 |
100.0 |
Table 6 Distribution of respondents Are you aware of most useful method for recovery (n=55)
According to this data, the greatest rate was 41.8% for physiotherapy participants (n=23), followed by 40% for both participants (n=22) and 18.2% for medicine (n=10). The majority of patients here demonstrated that physiotherapy treatment was crucial to returning to normal following a stroke. In addition to medicine, physiotherapy has been demonstrated to be an effective treatment method for stroke.
|
Different types of risk factors |
Chi-Square |
P-value |
|
63.51 |
0.001 |
Table 7 Association between with risk factors of CVD Vs Knowledge
While the pragmatic chi-square value and the means are currently lower, this realistic chi-square result raised 63.51 and 5% of the noteworthy certain chi-square remained 1.96. The alternative hypothesis remained putative after the null hypothesis was consistently disproved by risk variables and current CVD Stanzas knowledge. As a result, the conclusion was still incredibly significant, and the title was still associated with CVD risk factors vs knowledge.
|
Chi-Square |
P-value |
|
|
Attitude and practice Vs range of different age group |
128.47 (attitude) 59.12 (practice) |
0.005 |
|
0.017 |
Table 8 Association between with attitude and practice Vs range of different age group
Through 5% glassy of vital stated chi-square persisted 1.96 while remaining less than the observed chi-square significance, this realistic chi-square importance was 128.47 (attitude) and 59.12 (practice). This indicates that the alternative hypothesis remained recognized while the null hypothesis promoted banned attitudes and practices across a range of age clusters. The complaint went on to be quite serious, stating that there was a trapped connotation between the range of different age groups and the consequent attitude and practice.
Table 9 presents the relationship between gender and awareness of the most useful methods recovery at this research initiated. Scrutiny of Chi-Square was steered to reconnoiter the relationship between gender and awareness of recovery methods useful status with their most of them. Amongst these physiognomies, gender status (p = 0.02) and awareness of recovery status (p = 0.0001) are found to be statistically significant in relation to gender. Precisely, the findings reveal that gender status is significantly associated with awareness of recovery (χ2 = 2.29, p < 0.05), signifying gender that retain equated to awareness of recovery. Moreover, awareness of recovery methods most useful status presented a significant variance in gender levels (F = 8.86, p < 0.001).
|
Variables |
Categories |
Chi-Square |
P* Value |
|
Gender |
Male |
2.29 |
0.02 |
|
|
Female |
||
|
Aware of most useful method for recovery |
Medication |
8.86 |
0.0001 |
|
|
Physiotherapy |
||
|
|
Both |
Table 9 Relationship between awareness of most useful method for recovery and Gender (N = 55)
The aim of this study was to evaluate the knowledge, attitudes, and practices of discerning younger adults in the Mymensingh district regarding the precise threat implications of trendy CVD. On the other hand, KAP research at CVD threat influences in Mymensingh district and conference annexation/elimination norms continued to be the study populations. Fifty-five coconspirators persisted in the Mymensingh district, despite the fact that the study's target population was restricted due to the lack of quantitative education among people aged twenty to thirty-two. The study probe found that the accomplice's mean age was 25.98 (SD± 3.54) years, and the majority of candidates could handle being older than 20 to 25. The oldest participants in this study were between the ages of 31 and 35, or 3 years old, while the youngest participants were between the ages of 20 and 25. McGrath CMF et al. (2000) conducted a cross-sectional study to find out why 78 patients (mean age 57.8 ± 11.9 years, 23 men and 55 women) continued to believe in endowed enclosure erudition randomly. Siti Noor Khairina S. and Sakinah H. (2004) have attested to the substitute consequence. They determined that the mean age was ±62.1 and that their age range was between 30 and 50 years. As a result, upstairs dual studies were never the same for study. Gender revealed in this study that the accomplice expanses of men and women were indistinguishable. There was no racial bias, with males making up 25.5% (n=14) and females making up 74.5% (n=41) (Arshad et al., 2005). The findings of this study by the Uppermost Glassy of Education showed that the peak incidence of HSC and graduate degree applicants remained at 41.8% (n=23). The SSC accomplice standing rate remained at 9.1% (n=5). As an alternative, Evci ED and Memis S. (2007) reported that the male participants' highest quotient and his study's highest education level were both bachelor's degrees. The study's companions' income grade revealed that modest participants endured the highest amount, which was 63.6% (n=35). Bushnell CD and Goldstain LB, 2002, revealed their investigation into the highest income level while advanced accomplices maintained their highest quotient. As a result, the twofold investigation was still mostly speculative. Thus, dualistic research stayed comparable. This survey found that yes, accomplices continued to have the highest frequency, remaining at 61.8% (n=34), while no participants stood at 38.2% (n=21). Have you ever observed a brain attack or stroke? Participants in Ovbiagele B. et al.'s 2000 study remained at the top of the quotient. Combat research has not changed thus far. Similar to a heart attack, a cerebral stroke is an emergency that needs medical attention. According to this study, the highest frequency of yes accomplices remained at 56.4% (n=31), while the lowest frequency of no accomplices remained at 43.6% (n=24). According to Davis S. and Lees K. (2006), 89% of accomplices were still present.S
Do you know the risk factors for cardiovascular disease? According to this study, participants with hypertension maintained a maximum rate of 43.6% (n=24), while smoking companions maintained a subsequent maximum rate of 32.7% (n=18). According to research by Lipsky MMM and Bales RMM (2000), thrombosis and diabetes mellitus continued to be the leading factors, while Eliasziw M and Gates P (2000) demonstrated that vascular rupture and hypertension continued to be the leading factors. As a result, combat studies guarantee that hypertension remains an additional cause of risk in CVD. Do you know what the best course of action is for stroke? This analysis revealed that prevention accomplices stayed at 43.6% (n=24) and treatment contributors stood at the highest frequency of 56.4% (n=31). In 2001, Rowe AK and Frankel MR maintained the highest ratio for prevention. Are you aware of the most effective recovery technique? The study showed that the highest rate of physiotherapy aides remained at 41.8% (n=23), followed by equal aides at 40% (n=22) and medication at 18.2% (n=10). Yoon SS, Kwon YD Chang H. (2007) demonstrated her investigation that the highest quotient was sustained medicine and physical therapy treatment. There was a significant change in knowledge nicks about various risk variables (p<0.001), as well as in attitude and practice slashes compared to different genders (p = 0.005 and 0.017, respectively). Additionally, this study shows a strong positive correlation between attitude and practice grooves (r=+0.354, p<0.001), with women exhibiting superior attitude and practice.
The correlation test reveals a strong, if cautious, and hopeful relationship between the accused's overall attitude and practicing habits. This demonstrated that the level of practices would probably increase when their attitude stayed superior, and it quantified that the glassy of applications would predictably increase after their attitude remained better. Another study on the course of behavior modification supports this conclusion.10 It has been demonstrated that having a high level of knowledge without assistance did not declare the interactive amendment, and knowledge is not a significant factor in mutual attitude and practice.11 As the bent of the accused near be related with a deskbound lifestyle, shortage of workout, underprivileged diet with disquieting lifespan, these features turn out to be exciting for them to gadget and sustain a strong usual of successful.12 Around ought to be additional crusades concerning strong regimes arranged estate towards ratify the young group concerning nil illnesses and allowed from the CVD hazard features. A small numerical difference was observed here and consistent with other studies of morbidity and mortality in stroke risk factors and illness in young adults populations.
This study suggests recognizing their effective methods for reducing the prevalence of CVD. Although the knowledge levels were appealingly high, there is no correlation between the scenario and the glassy attitude or practices. With regard to attitude and practice, there are notable differences between males and females, but there is also a big modification among the numerous talents trendy footings of knowledge. Regardless of how uniform the positive relationship between attitude and practice is, it reflects an unbiased, small link that suggests the practice may be improved if attitude is restored. Thus, this cross-sectional study's unusual limitation Future research continues to support an improved impost. In my opinion, the study is a good starting point for future research on CVD in Bangladeshi young adults, and it is recommended that more research be done on the areas that require the greatest attention in terms of risk factors and medication.
The authors express their sincere gratitude to all collaborating medical professionals for their invaluable time and helpful assistance.
The authors declared no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
This research study was not supported by any funding or sponsoring agency. Funds were provided by researchers.

©2024 Azad, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.