eISSN: 2373-6372


Short Communication Volume 16 Issue 3
1Anwar Khan Mordern Hospital, Bangladesh
2Sir Salimullah Medical College, Bangladesh
3Labaid Specialized Hospital, Bangladesh
4Mymensingh Medical College, Bangladesh
5Labaid Specialized Hospital, Bangladesh
Correspondence: Dr. Ahmed Sarwar Murshed, Anwar Khan Mordern Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Received: April 29, 2025 | Published: June 26, 2025
Citation: Murshed AS, Karim F, Rahman S, et al. Treatment with combination transarterial chemoembolization and lenvatinib plus sequential microwave ablation improves survival in patients with unresectable large hepatocellular carcinoma beyond up-to-7 criteria. Gastroenterol Hepatol Open Access. 2025;16(3):83-85. DOI: 10.15406/ghoa.2025.16.00613
The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined with Lenvatinib plus sequential microwave ablation (MWA) for the treatment of patients with large hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) beyond up-to-seven criteria.
Methods: This multicenter prospective study included 135 patients diagnosed with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer beyond Upto 7(BCLC B2) between January 2015 and January 2022. Participants were grouped into: i) Transarterial Chemoembolization with Lenvatinib plus sequential Microwave ablation group (TLM, n=47), and ii) Transarterial Chemoembolization and Microwave ablation group (TM, n=88). Each group was subdivided based on the largest tumor diameter: a) 7-8 cm, b) 8-10 cm, and c) >10 cm. In the TLM group, Lenvatinib was administered 7 days post-transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE), followed by Microwave Ablation (MWA) after 21 days. Lenvatinib was resumed after recovery from MWA. The TM group underwent MWA 7 day’s post-TACE. Progression-Free Survival (PFS), Overall Survival (OS), and complications were assessed.
Results: Technical success of combined transarterial chemoembolization and Microwave Ablation was achieved in all patients (100% either in single or multiple sessions). Follow-up MRI/CT was done to assess the treatment response after one month. The median follow up period was 48.5 months. The TLM group had longer PFS than the TM group (median, 17.32 vs. 6.3 months, p < 0.001; median.1,3,5 year cumulative overall survival of patients in TM group: 7-8 tumor subgroup: 96%, 72 %, 42%; in 8-10 cm subgroup:87%, 45%,18%; in more than 10 cm tumor sub group: 48%, 24%, 3% and in TLM group: 7-8 tumor sub group: 95%, 77%, 51%; in 8-10 tumor sub group: 92%, 59%, 32%; in more than 10 cm tumor sub group: 61%, 34%, 9%. There was no treatment related death. Minor complications like pain, fever, nausea occurred in 13% cases while major complications such as Hepatic failure, hemorrhage, pleural effusion occurred in 1% cases. The occurrence of major complications were seen mainly in Cirrhosis Child Pugh B patients irrespective of TLM or TM groups.
Conclusion: The combination of TACE, Lenvatinib, and sequential MWA improves PFS and OS in patients with large unresectable HCC beyond the up-to-seven criteria, with a high safety profile.
Keywords: Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Transarterial Chemoembolization, Lenvatinib, Microwave Ablation, Survival Analysis
According to Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) guidelines, TACE remains the treatment of choice for stage B2 tumors. Combining microwave ablation with TACE may improve the control of larger tumors, while tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) can prevent tumor recurrence. This study, therefore, explores the efficacy of combining TACE with MWA and TKI (Lenvatinib) in patients with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Beyond upto 7 criteria.
Aim
This study aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) combined with Lenvatinib plus sequential Microwave Ablation (MWA) for the treatment of patients with large Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Barcelona clinic liver cancer stage B2 (beyond up-to-7 criteria).
Methods
This multi-center study included 135 patients with Stage B2 HCC from January 2015 to January 2022. The patients' ages ranged from 28 to 82 years, and the study population included 102 males and 32 females. 112 patients had Child-Pugh A cirrhosis, and 23 had Child-Pugh B cirrhosis. The maximum tumor diameter ranged from 7 to 12 cm, and the maximum tumor number was 5. 95 patients had single tumor while 40 patients had multiple tumor only patients with at least 50% of liver parenchyma free from malignant tumors were included.
Patients were divided into two groups:
i) TACE-Lenvatinib-MWA (TLM) group (n=47)
ii) TACE-MWA (TM) group (n=88)
Each group was further subdivided based on the size of the largest tumor:
a) 7-8 cm tumor group
b) 8-10 cm tumor group
c) >10 cm tumor group
In the TLM group, Lenvatinib was started 7 days post-TACE, and MWA was performed 21 days after Lenvatinib administration. Lenvatinib treatment was restarted after recovery from MWA and continued until tumor recurrence. In the TM group, MWA was performed 7 days after TACE, and recurred tumors were re-ablated.
Progression-free survival (PFS), cumulative overall survival (OS), and treatment-related complications were compared between the groups.
Results
Technical success of combined Transarterial Chemoembolization and Microwave Ablation was achieved in all patients (100% either in single or multiple sessions). Follow-up MRI/CT was used to assess treatment response one month post-treatment. The median follow-up period was 48.5 months.
The TLM group had longer PFS than the TM group (median, 17.32 vs. 6.3 months, p < 0.001). The 1, 3, and 5-year cumulative overall survival rates for patients in the TM group were:
The 1, 3, and 5-year cumulative survival rates for patients in the TLM group were:
There was no treatment-related death. Minor complications such as pain, fever, and nausea occurred in 13% of cases, while major complications such as hepatic failure, hemorrhage, and pleural effusion occurred in 1% of cases (Figure 1, Table 1).
|
Months |
% Median Survival |
|||||
|
TACE + MICROWAVE + LENVATINIB |
TACE + MICROWAVE |
|||||
|
7-8 cm |
8 - 10 cm |
> 10 cm |
7-8 cm |
8 - 10 cm |
> 10 cm |
|
|
0 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
|
6 |
100 |
100 |
61 |
100 |
100 |
92 |
|
12 |
95 |
92 |
52 |
96 |
87 |
48 |
|
18 |
88 |
82 |
47 |
85 |
78 |
42 |
|
24 |
82 |
75 |
41 |
80 |
69 |
36 |
|
30 |
80 |
62 |
38 |
75 |
58 |
30 |
|
36 |
77 |
59 |
34 |
72 |
45 |
24 |
|
42 |
72 |
48 |
27 |
66 |
37 |
20 |
|
48 |
65 |
37 |
19 |
60 |
31 |
12 |
|
54 |
58 |
32 |
15 |
50 |
26 |
8 |
|
60 |
51 |
28 |
9 |
42 |
18 |
3 |
Table 1 Survival Outcomes
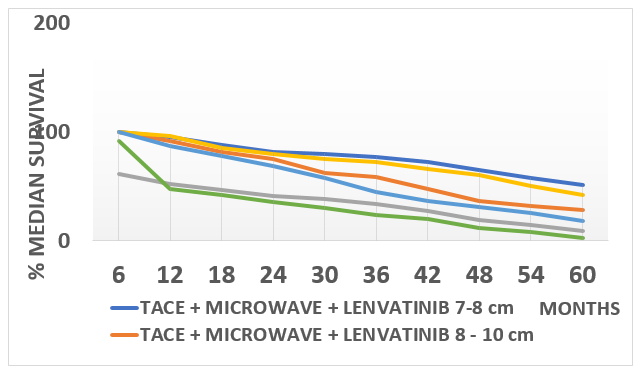
Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier Analysis - Median Survival Outcomes in TLM vs. TM Groups: A Comparative Analysis of Tumor Size Subgroups Over Time.
Case Illustration
Transarterial chemoembolization has been the treatment of choice for decades for Barcelona clinic liver cancer stage B1 and B2. A Recent study1 revealed that Microwave ablation can effectively ablate 8 cm tumors. Yet, Transarterial chemoembolization can induce tissue hypoxia leading to upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor, which may cause incomplete tumor necrosis and recurrence. Moreover, incomplete Microwave ablation can activate hypoxia-inducible factor1-alpha/ vascular endothelial growth factor a pathway, potentially contributing to rapid tumor growth. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor expression and tumor progression can be ceased.2 So, if we combine Tyrosine kinase inhibitors with Thermal ablation or TACE we certainly can get better progression free survival and overall survival. A pilot study on the use of combination of RFA and Lenvatinib in the management of Barcelona Clinic Liver cancer stage B has yielded 74% 2 yr Overall Survival in RFA-Lenvatinib group while it is only 25% in Lenvatinib group in BCLC B2.3 Another retrospective cohort study in BCLC Beyond upto 7 patients showed that Median OS in TACE TACE plus TKI group is 28 months while in TACE group it is only 12 months4 On top of that, various meta analyses5 on combination of transarterial chemoembolization and thermal ablation showed better result in treating Hepatocellular Carcinoma Barcelona clinic Liver Cancer stage B1 and B2 than treated individually. The result of Barcelona clinic liver cancer stage B1 is far better than Barcelona clinic liver cancer stage B2, but much studies were not carried out on microwave ablation stage B2 patients. Based on the above findings, it can be hypothesized that if tyrosine kinase inhibitor could be added with Transarterial chemoembolization-Microwave ablation combination, better survival outcome in Barcelona clinic liver cancer stage B2 patients can be achieved. Because, transarterial chemoembolization decrease the tumor volume as well as occludes blood vessels within the tumor which in turn decrease the heat shrink effect during Microwave ablation. Hence MWA can enhance the rate of complete ablation of a large tumors and TKIs inhibit VEGF and hault tumor recurrence. A retrospective study found out that Combination of TACE with Lenvatinib with sequential MWA can significantly increase the progression free survival and overall survival of patients with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Beyond upto 7 than treated only with Trans arterial Chemoembolization-Microwave Ablation combination.2,6 Our aim was to carry out a prospective study to investigate the efficacy and safety of trans-arterial chemoembolization combined with Lenvatinib plus sequential microwave for the treatment of patients with large Hepatocellular Carcinoma beyond upto 7 criteria in Bangladesh. Progression-Free Survival is significantly high in TACE-Lenvatinib with sequential Microwave Ablation group (TLM) than the TACE-MWA group TLM (17.32 months) vs. TM (6.3 months), p < 0.001. Overall survival was also significantly higher in TLM group than TM group. The prognostic analyses showed that the treatment allocation and the maximum tumor size (Poor in tumor size more than 10 cm) and number (Better in Single tumor than multiple tumors), extend of cirrhosis (Child Pugh A was better than Child Pugh B) were independent predictors of PFS and OS. The study also revealed that TLM treatments were well tolerated in advanced HCC patients. The rates of major complications in patients who underwent TLM therapies were similar to those in patients who underwent TM therapies, while the rates of minor complications were significantly lower.
One weakness we have noticed that our patient cohort should have been more in number to yield a more concrete outcome. We warrant more studies on combination of TACE -Lenvatinib and sequential MWA.
TACE-Lenvatinib-MWA can prolong the Progression-Free Survival and Overall Survival of patients with large hepatocellular carcinoma beyond up-to-seven criteria with a high safety ratio.
We thank the Bangladesh Society for Liver Cancer Treatment & Research and Everest Pharmaceuticals Ltd. for their support of this research.
None.

©2025 Murshed, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.